RESTful API,你真理解了吗?

什么是RESTful API?
RESTful API并不是什么框架,他也并不是某段啥代码,他单纯的就是一种规范,一个标准。一旦涉及带规范、标准,就是一个很空泛概念,一开始很难理解真正的特点,然后就很难将其与传统的API区分开来;
RESTful API与传统API的区别
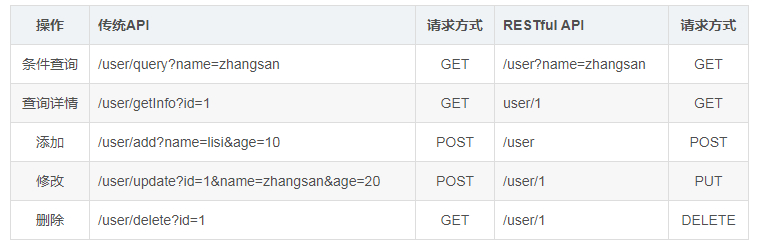
- 传统API的url
代表的是一种行为;如上图的查询/user/query,通过url就可以知道当前的接口适用于查询操作的; - RESTful API的url
表示的是资源;如上图的接口地址,多次出现/user/1;/user/1表示着用户ID为1的这个用户资源,1000个用户,就有1000个请求地址,也就对应着1000个资源;根据url地址,我们没有办法知道当前接口的操作是什么;具体接口的功能是通过这个接口的请求方式(method)来进行标识;如同为/user/1的资源:- Method是GET的时候,标识的就是查询id为1的用户;
- Method是PUT的时候,就是修改;
- Method是DELETE时就是删除这个资源了;
SpringBoot中用于定义RESTful API的常用注解
@RestController标明对应的Controller用于提供RESTful API@RequestMapping用于映射http的url到对应的java方法上;其还有如下变种的方法@GetMapping等价于 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)@PostMapping等价于 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)@PutMapping等价于 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)@DeleteMapping等价于 @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@RequestParam映射请求参数到java方法的参数@PageableDefaule指定分页参数默认值@PathVariable将path中的变量映射到java方法的参数;如GetMapping("/user/{id}"),当请求/user/1的时候id会映射为1,当请求/user/100时id会映射为100- @RequestBody 映射请求体到java方法的参数
示例
-
pom.xml
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> </dependency>- 以下是使用RESTful API 基于以上的示例及以上的注解,编写的测试代码
// 用户对象 @Data @AllArgsConstructor public class User { private Integer id; private String username; private String nickName; private Integer age; private String password; }import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonView; import com.lupf.springbootrestfulapi.dto.User; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable; import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort; import org.springframework.data.web.PageableDefault; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * @author lupf * @date 2020/7/13 9:16 * @desc */ @RestController @RequestMapping ("/user") @Slf4j public class UserController { /** * 等价于 @RequestMapping (value = "user", method = RequestMethod.GET) * * @param name * @param pageable * @return * @RequestParam 用于映射请求参数 * @PageableDefault 用于配置默认的分页数据 */ @GetMapping public List<User> getUserByName(@RequestParam ("username") String name, @PageableDefault (page = 1, size = 10, sort = {"age"}, direction = Sort.Direction.DESC) Pageable pageable) { log.info("username:{}", name); log.info("pageable.getPageSize():{}", pageable.getPageSize()); log.info("pageable.getPageNumber():{}", pageable.getPageNumber()); log.info("pageable.getSort():{}", pageable.getSort()); User user = new User(1, name, "xiaoxx", 10, "123456"); List<User> users = new ArrayList<>(); users.add(user); return users; } /** * 根据ID获取用户的详细信息 * * @param id * @return */ @GetMapping ("/{id:\\d+}") public User getUserInfoById(@PathVariable Integer id) { log.info("username:{}", id); User user = new User(1, "zhangsan", "xiaoxx", 10, "123456"); return user; } /** * 添加用户信息 * Spring会将请求中content中的json对象转换为一个User对象 * * @param user */ @PostMapping public void addUser(@RequestBody User user) { log.info("user:{}", user); } /** * 根据用户ID修改用户数据 * * @param id 修改的用户对应的ID * @param user 待修改的用户信息 */ @PutMapping ("/{id:\\d+}") public void updaste(@PathVariable Integer id, @RequestBody User user) { log.info("update user id:{}", user.getId()); log.info("update user:{}", user); } /** * 根据用户id删除 * * @param id */ @DeleteMapping ("/{id}") public void delete(@PathVariable Integer id) { log.info("delete user id:{}", id); } }
接口测试用例
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
@RunWith (SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class SpringbootRestfulApiApplicationTests {
@Autowired
WebApplicationContext wac;
MockMvc mockMvc;
/**
* 每个测试用例执行之前都会执行这一段方法
*/
@Before
public void setup() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(wac).build();
}
@Test
public void queryUserSuccessByUserName() throws Exception {
String responseStr = mockMvc.perform(
// 请求构建对象
MockMvcRequestBuilders
// 指定请求的restful api的地址
// .get 就是表示发送get方法
.get("/user")
// 指定请求内容的格式
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
// 参数
.param("username", "zhangsan")
// 页面
.param("page", "1")
// 分页的大小
.param("size", "10")
// 排序
.param("sort", "age,desc"))
// 指定响应的预期状态码
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
// 指定响应预期的内容
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.length()").value(1))
// 获取到响应数据
.andReturn().getResponse().getContentAsString();
log.info("return string:{}", responseStr);
// jsonPath : https://github.com/json-path/JsonPath
}
@Test
public void queryUserSuccessByIdSuccess() throws Exception {
String responseStr = mockMvc.perform(
// 请求构建对象
MockMvcRequestBuilders
// 指定请求的restful api的地址
// .get 就是表示发送get方法
.get("/user/1")
// 指定请求内容的格式
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
// 指定响应的预期状态码
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
// 指定响应预期的内容
// 要求返回的对象的用户名为:zhangsan
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.username").value("zhangsan"))
// 获取到响应数据
.andReturn().getResponse().getContentAsString();
log.info("return string:{}", responseStr);
}
@Test
public void queryUserSuccessByIdFail() throws Exception {
String responseStr = mockMvc.perform(
// 请求构建对象
MockMvcRequestBuilders
// 指定请求的restful api的地址
// .get 就是表示发送get方法
.get("/user/mm")
// 指定请求内容的格式
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
// 指定响应的预期状态码为4xx
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().is4xxClientError())
// 获取到响应数据
.andReturn().getResponse().getContentAsString();
log.info("return string:{}", responseStr);
}
@Test
public void addUserSuccess() throws Exception {
String content = "{\"username\":\"wangwu\",\"age\":25,\"nickName\":\"wuwu\",\"password\":\"123321\"}";
mockMvc
.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/user").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8).content(content))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
}
@Test
public void updateUserSuccess() throws Exception {
String content = "{\"username\":\"wangwu\",\"age\":30,\"nickName\":\"wwuwu\",\"password\":\"789456\"}";
mockMvc.perform(
//
MockMvcRequestBuilders
// 请求对象
.put("/user/1")
// 请求内容的个数
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
// 请求数据
.content(content))
// 响应状态要求
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
}
@Test
public void deleteUserSuccess() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.delete("/user/1").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
}
}
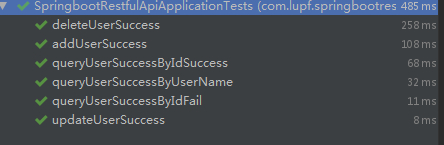
只要理解了对数据的操作转换为资源的操作,RESTful API就比较好理解了。
 IDEA
IDEA
 Java
Java
 SpringBoot
SpringBoot
 面试题
面试题
 工具
工具
 程序员导航
程序员导航
 JDK
JDK