SpringBoot整合sharding-jdbc:水平分库、水平分表

前言
前文中,测试到了单库下的水平分表;水平分表其实已经可以解决大部分的数据库压力了,但是往往单机是会存在性能瓶颈的,所以,当出现数据量大,访问频率高的时候,往往就会出现单机器的CPU、内存高负荷的情况;因此,就会在基于单库的水平分表基础上去考虑水平分库、水平分表;这样将数据分散再多台机器的多个表中;从而降低单机器的硬件性能压力;
需求
模拟电商系统中,基于店铺id的水平分库,基于商品id的水平分表
-
数据库结构
## 商品信息表 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `product_info1`; CREATE TABLE `product_info1` ( `product_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品ID', `product_title` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品标题', `product_desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品描述', `product_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品价格', `shop_id` bigint(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺id', PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `product_info2`; CREATE TABLE `product_info2` ( `product_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '商品ID', `product_title` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品标题', `product_desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品描述', `product_price` decimal(10, 2) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品价格', `shop_id` bigint(20) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺id', PRIMARY KEY (`product_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; ## 点破信息表 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `shop_info1`; CREATE TABLE `shop_info1` ( `shop_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '店铺id', `shop_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺名称', `shop_desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺描述', `shop_type` int(2) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺的类型 目前用于对店铺类型进行分表的一句', PRIMARY KEY (`shop_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `shop_info2`; CREATE TABLE `shop_info2` ( `shop_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '店铺id', `shop_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺名称', `shop_desc` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺描述', `shop_type` int(2) NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '店铺的类型 目前用于对店铺类型进行分表的一句', PRIMARY KEY (`shop_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic; # 共享表 广播表 # 店铺类型 DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `shop_type_info`; CREATE TABLE `shop_type_info` ( `type_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '店铺类型', `type_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci NULL DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '类型名称', PRIMARY KEY (`type_id`) USING BTREE ) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8 COLLATE = utf8_general_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;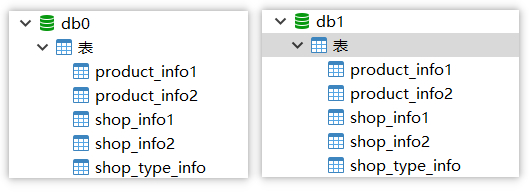
SpringBoot整合
依赖
<!-- sharding-jdbc整合spring的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0-RC1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql 数据库连接 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
使用generator生成mybatis的映射信息
可参考博客: https://blog.csdn.net/lupengfei1009/article/details/87986987
启动类添加mybaitis的扫描
记得根据你实际的地址填写
@MapperScan("com.lupf")
配置sharding-jdbc的分库分表策略
-
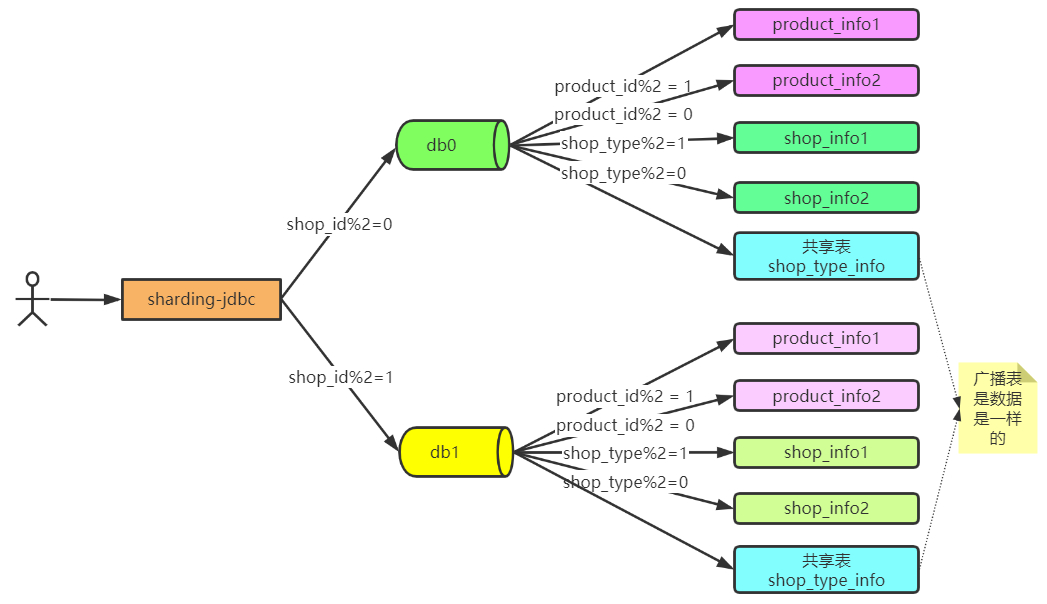
策略说明
- 所有的商品优先以店铺id进行水平分库
- 到库之后,所有商品根据id进行水平分表
- 店铺信息到库之后,根据店铺类型进行水平分表
- 店铺类型为共享表
最终要实现的效果如下
-
properties配置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapping/*.xml server.port=7777 # 设置数据源 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=db0,db1 # db0的基本信息 这里的db0要和上面的配置要保持一直 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db0.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.221:3306/db0?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false&maxReconnects=15000&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db0.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db0.password=123456 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db0.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db0.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # db1的基本信息 这里的db1要和上面的配置要保持一直 # 这里是将两个库都放置在了一个mysql中,正常的实际开发中是不会这么做的 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.221:3306/db1?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false&maxReconnects=15000&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.username=root spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.password=123456 spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 设置数据库分库的表达式 spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=db$->{shop_id % 2} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=shop_id # 指定分表的规则 # db$->{0..1}指明库的取值范围 db0和db1 会根据上面给定的规则,计算出库名 如果没有传递shop_id 这里会报错 # product_info$->{0..1}指明了表的取值范围product_info0和product_info1;会根据下面给的运输规则$->{product_id % 2 + 1}得到 spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.product_info.actual-data-nodes=db$->{0..1}.product_info$->{0..1} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.product_info.key-generator.column=product_id spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.product_info.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.product_info.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=product_info$->{product_id % 2 + 1} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.product_info.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=product_id spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.shop_info.actual-data-nodes=db$->{0..1}.shop_info$->{0..1} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.shop_info.key-generator.column=shop_id spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.shop_info.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.shop_info.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=shop_info$->{shop_type % 2 + 1} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.shop_info.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=shop_type # 用户表,这里不进行分库,直接将数据保存在db0中 spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user_info.actual-data-nodes=db0.user_info$->{0..1} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user_info.key-generator.column=user_id spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user_info.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user_info.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=user_info$->{user_id % 2 + 1} spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.user_info.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=user_id ## 指明广播表 公共表 spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=shop_type_info spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
测试
广播表的操作
-
插入
@Resource ShopTypeInfoPOMapper shopTypeInfoPOMapper; @Test public void insert(){ ShopTypeInfoPO shopTypeInfoPO = new ShopTypeInfoPO(); shopTypeInfoPO.setTypeId(1); shopTypeInfoPO.setTypeName("普通店铺"); shopTypeInfoPOMapper.insert(shopTypeInfoPO); }测试日志
: Logic SQL: insert into shop_type_info (type_id, type_name) values (?, ?) : Actual SQL: db0 ::: insert into shop_type_info (type_id, type_name) VALUES (?, ?) ::: [1, 普通店铺] : Actual SQL: db1 ::: insert into shop_type_info (type_id, type_name) VALUES (?, ?) ::: [1, 普通店铺]发现其往两个库里面同时插入了相同的数据
店铺表测试
-
分发策略
- 根据shop_id分发到不同的库
- 到库之后,根据不同的类型分发到表
-
去掉insert中的shop_id字段
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.lupf.tmall02.po.ShopInfoPO"> insert into shop_info (shop_name, shop_desc, shop_type) values (#{shopName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{shopDesc,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{shopType,jdbcType=INTEGER}) </insert> -
插入
@Resource ShopInfoPOMapper shopInfoPOMapper; @Test public void insert(){ Random random = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { ShopInfoPO shopInfoPO = new ShopInfoPO(); //shopInfoPO.setShopId(0L); shopInfoPO.setShopName("店铺名称"); shopInfoPO.setShopDesc("店铺描述"); shopInfoPO.setShopType(random.nextInt(2)+1); shopInfoPOMapper.insert(shopInfoPO); } }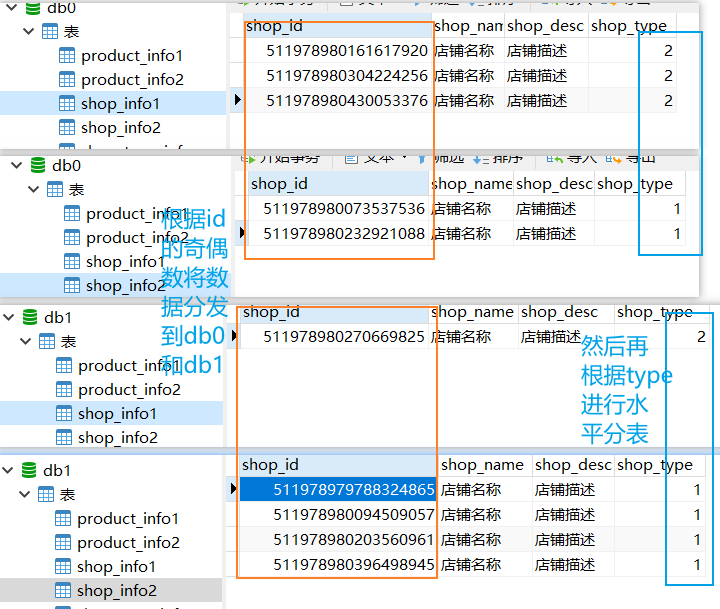
商品表测试
-
分发策略
- 根据店铺id进行水平分库
- 到库之后,根据商品id进行水平分表
-
去掉insert中的product_id字段
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.lupf.tmall02.po.ProductInfoPO"> insert into product_info ( product_title, product_desc, product_price, shop_id) values (#{productTitle,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{productDesc,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{productPrice,jdbcType=DECIMAL}, #{shopId,jdbcType=BIGINT}) </insert> -
测试用例
@Resource ProductInfoPOMapper productInfoPOMapper; @Test public void insert(){ Random random = new Random(); // 所有当前已经插入的店铺的id Long[] shopIds = new Long[]{ 511978980161617920l, 511978980304224256l, 511978980430053376l, 511978980073537536l, 511978980232921088l, 511978980270669825l, 511978979788324865l, 511978980094509057l, 511978980203560961l, 511978980396498945l }; for (int i=0;i<100;i++) { ProductInfoPO productInfoPO = new ProductInfoPO(); //productInfoPO.setProductId(0L); productInfoPO.setProductTitle("商品名称"); productInfoPO.setProductDesc("商品描述"); productInfoPO.setProductPrice(new BigDecimal(random.nextInt(1000))); productInfoPO.setShopId(shopIds[random.nextInt(shopIds.length)]); productInfoPOMapper.insert(productInfoPO); } }
链合查询测试
- Join
-
不带条件
select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info as s LEFT JOIN product_info as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_i操作日志
: Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info1 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info1 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db0 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info1 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db0 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info1 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db0 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db0 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC由于没有任何条件,所以穷举的各个库各个表的各种情况
-
主表带分库条件
select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info as s LEFT JOIN product_info as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 and s.shop_type=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id日志
: Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info1 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info1 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC由于带了分库参数,所以就只关联了db1库中的表
-
主表带分库、分表
select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info as s LEFT JOIN product_info as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 and s.shop_type=1 and p.product_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id日志
: Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info1 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 and s.shop_type=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC : Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 and s.shop_type=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id ORDER BY shop_id ASC由于带了主表分库分表的字段,所以就只会使用主表和其他表进行关联
-
主表,副表都带分库、分表字段
select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info as s LEFT JOIN product_info as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 and s.shop_type=1 and p.product_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id日志
Actual SQL: db1 ::: select s.shop_id,COUNT(*) from shop_info2 as s LEFT JOIN product_info2 as p on s.shop_id=p.shop_id where s.shop_id=1 and s.shop_type=1 and p.product_id=1 GROUP BY s.shop_id由于条件可以明确的定位到主表和副表分别对应了那张表的数据,因此就只会使用对应表的数据进行关联
-
其实和单库的水平分表没有什么区别;唯一麻烦的就是sharding-jdbc的分片规则更加复杂了,只要配置好了分片规则,对于上层应用来说,完全是透明的。
标题:SpringBoot整合sharding-jdbc:水平分库、水平分表
作者:码霸霸
地址:https://blog.lupf.cn/articles/2020/09/14/1600068985256.html
 IDEA
IDEA
 Java
Java
 SpringBoot
SpringBoot
 面试题
面试题
 工具
工具
 程序员导航
程序员导航
 JDK
JDK